Animals Producers and Consumers
Living organisms can be grouped based on what they look like. when organisms are thought about as living together it is helpful to group them based on what they eat.There are two groups : One group that produces food and the other group that consumes food.
Producers
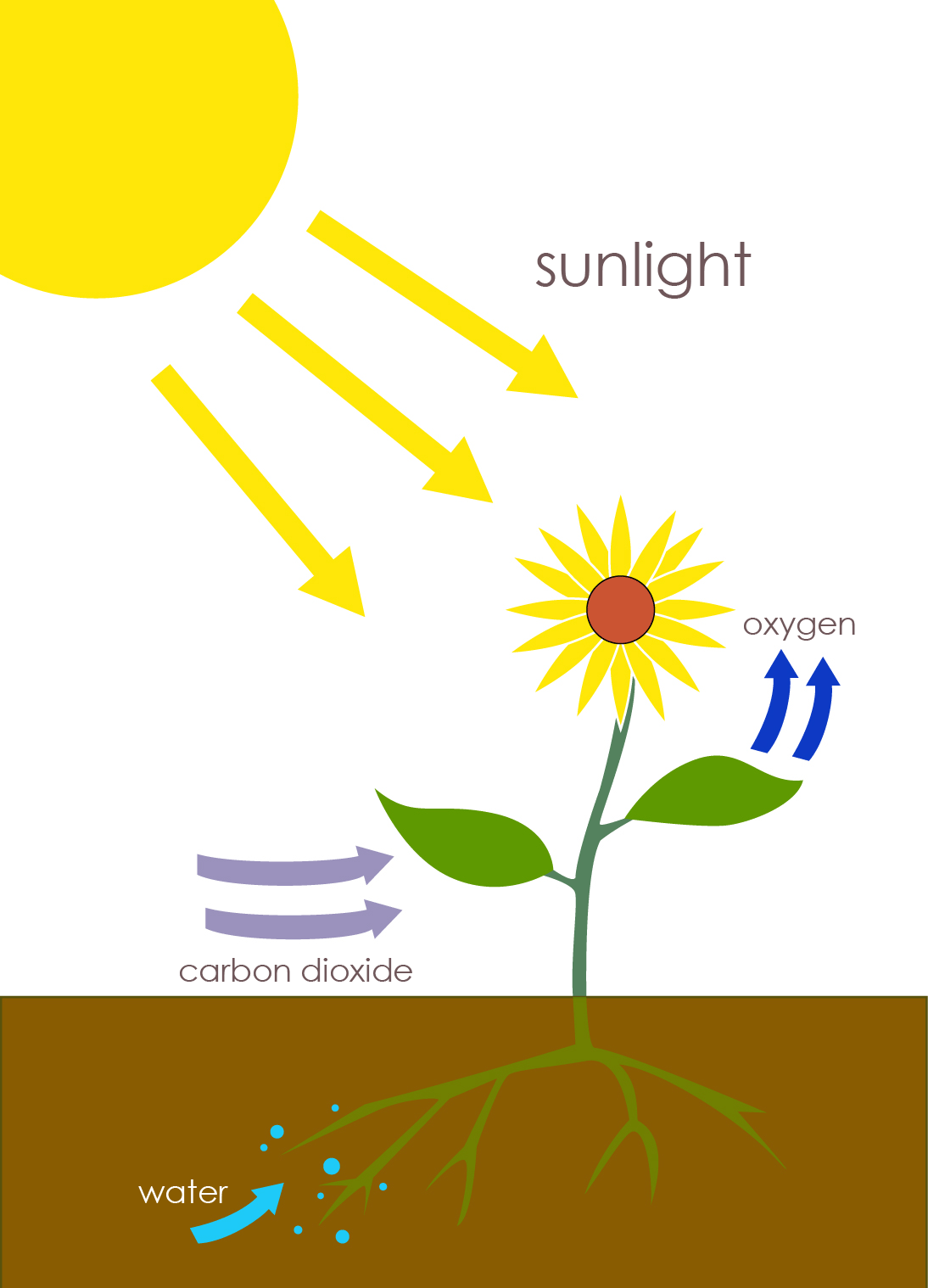
Primary producers are organisms in an ecosystem that produce biomass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). Producers make the food for all the other members of the community, they make their own food from simple substances carbon dioxide and water. Pants use light to make sugars from carbon dioxide and water.Bacteria are also producers. some use light but most use chemical reactions to get their energy.
Consumers
All animals are consumers. They cannot make their own food so they have to eat or consumer it.A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.
Secondary consumers are carnivores. They eat herbivores.
A carnivore /ˈkɑrnɪvɔər/ meaning 'meat eater' (Latin, caro meaning 'meat' or 'flesh' and vorare meaning 'to devour') is an organism that derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of animal tissue, whether through predation or scavenging.
Tertiary consumers are small carnivores that eat secondary consumers. They are sometimes called top carnivores.
Decomposers are microbes that feed on dead and decaying material. Most of these are bacteria and fungi. The decomposers turn the dead and decaying material into nutrients that the producers use to produce food.
 |
| Most bears are omnivores |
Omnivores are animals that eat a mixture of plant and animal foods. some omnivores eat plants most of the time.
Credit : image from google , wikipedia and wikimedia

.jpg)












